Bloxxgame 1
The positive feedback from students about their improved understanding of blockchain and Bitcoin after playing Playcoin encouraged us to continue developing a gamified learning environment. Read the article about Playcoin to learn more about the original concept of a learning game and how Bloxxgame evolved from Playcoin.
With financial support from the FHNW Teaching Fund, we developed the first prototype of Bloxxgame in 2019. We kept to the principle of balancing clarity and precision.
Organised playground with boxes
The software game allowed us to make the hashing and signing algorithms more realistic without losing clarity. The core idea was to visualize a blockchain that could be seen and played like a board game on a single screen. All data and activities were structured in nine interconnected boxes. Players could act as nodes and interact with each other through this interface.
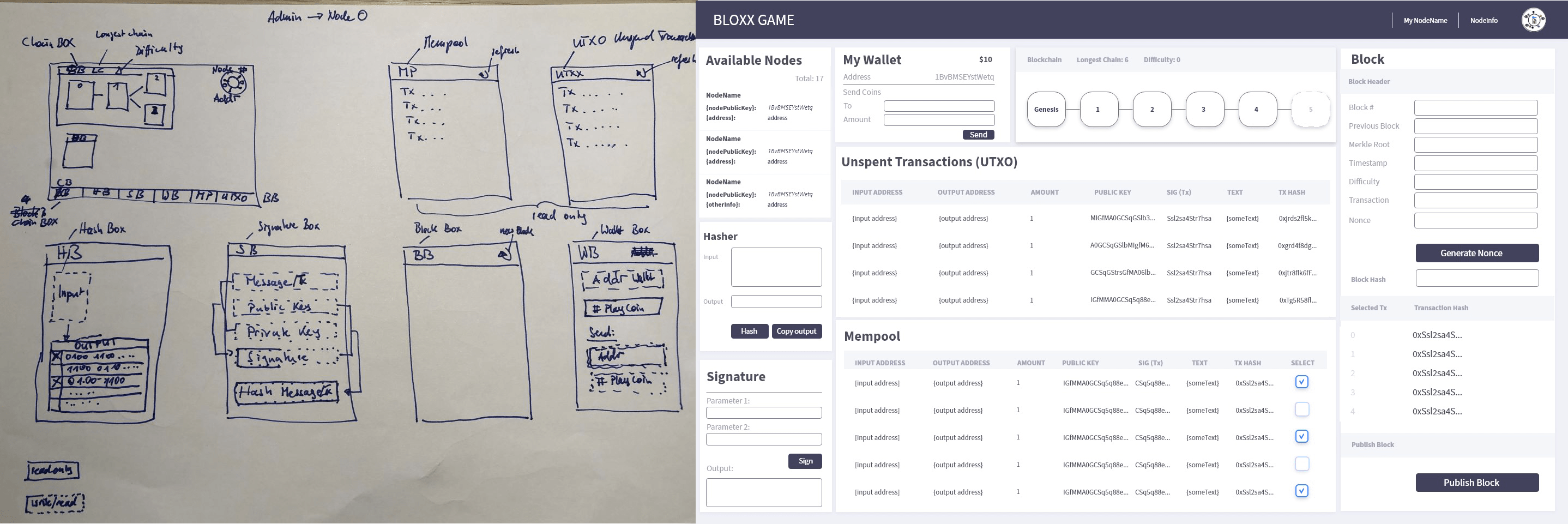
With hindsight, we can say that this first prototype was a great success. It was very simple, and the students enjoyed playing with it. All basic tasks could be performed: Hashing data, creating transactions, signing and verifying transactions, monitoring the mempool, creating blocks and receiving block rewards, etc.
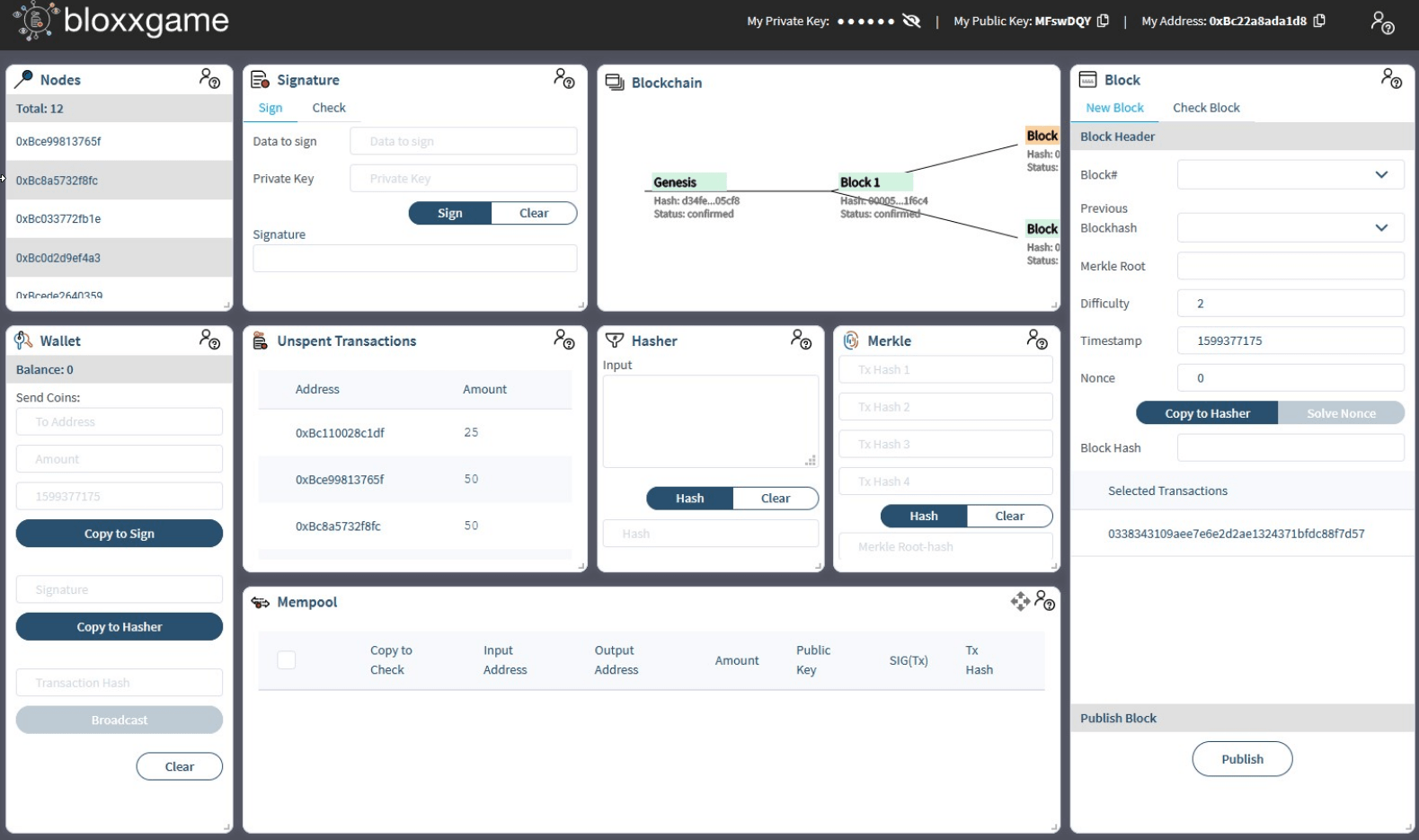
Learning by mistakes
Bloxxgame did not prevent players from making elementary mistakes. They could use wrong keys for signing, change data after hashing, spend too much money from their wallets or create blocks with double spends, etc.
Therefore, players had to use Bloxxgame’s control features to ensure that they only used valid transactions or created their blocks on a valid branch of the blockchain.
Nevertheless, it was possible for a game session with Bloxxgame to end in a big “mess” and there was no way to fix it.
The big advantage of Bloxxgame was that the teacher could reset the game very easily and quickly and everyone could start from scratch.
Visualization
The basic idea of the consensus algorithm, implicit confirmations of blocks and the creation and resolution of forks was well visualised in the blockchain box.
The block miner box clearly showed what a proof of work is when players had to wait for the solver to search for a nonce to reach the right difficulty level.
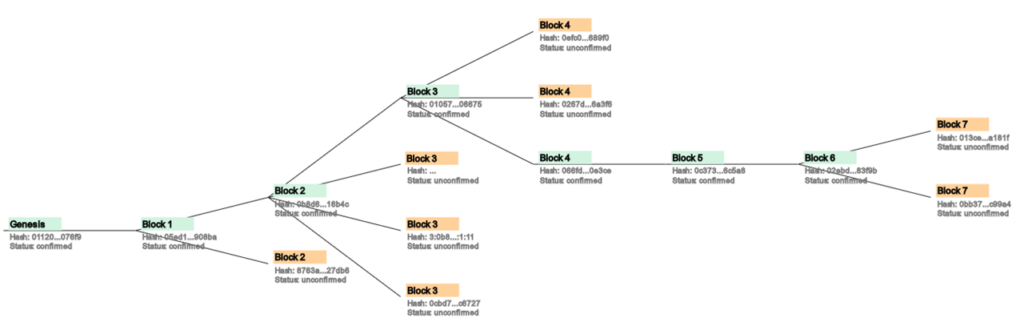
Bloxxgame changed the classroom atmosphere
The switch to a software blockchain game brought a major change to the classroom. Playcoin was only playable in groups, as the different tasks required several heads and many hands simultaneously. Bloxxgame, however, became a single-player game. Sharing a screen with other players was possible, but not as much fun as with Playcoin. In classroom situations, however, the class groups were able to solve problems together. As everyone was on the same blockchain, the dynamic was even greater.
Bloxxgame made distance learning possible, Covid-19 made it mandatory
When distance learning became mandatory in spring 2020 due to Covid-19, Bloxxgame was a big win for online blockchain education. Students could access Bloxxgame from home and see their transactions and blocks appear on the blockchain. The teacher had complete control over the game just like in the classroom. Bloxxgame was an almost perfect illusion of a blockchain.
Feedback from students indicated that Bloxxgame was a good teaching tool and a real improvement over Playcoin. We also evaluated teaching outcomes and initiated our first collaborations with other schools and teachers who used Bloxxgame in their teaching.
Limitations of Bloxxgame 1
- Lack of Persistence: If a player refreshed their browser, they would lose access to their node. Although they could reconnect to the game, they had to start over with a new node address and new keys. Only the teacher (master) had a fixed node address and could access a game again.
- Error-Friendly Design: Players could make all kinds of mistakes, intentionally designed to promote learning by doing. The software didn’t prevent overspending, errors in hashing, or incorrect solutions to the hash puzzle. This was crucial for them to truly understand how the blockchain mechanism works to ensure security. However, this error-friendly approach required significant support from teachers.
- Teacher’s Role: The teacher had to ensure a “correct” game, validating blocks and ensuring the main-chain only contained valid transactions and blocks. This required significant attention and a good understanding of the tool.
- Server Infrastructure: A server infrastructure was required since we had not implemented a peer-to-peer network where all nodes stored the game locally.
Overall, Bloxxgame 1 was an effective teaching tool, but it was not intended to be passed on to other teachers. Bloxxgame 3 (version 2024) has eliminated these and many other shortcomings.